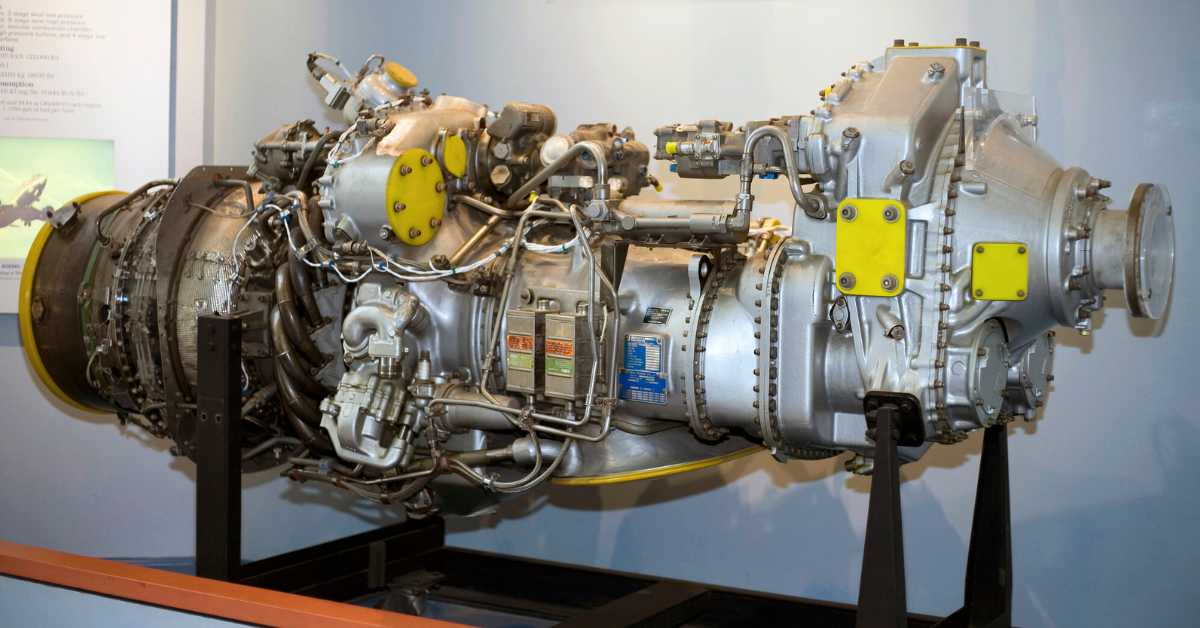
Aircraft are one of the most popular modes of transportation in the world. But, have you ever wondered how an aircraft can fly with such a heavy weight? There are many different types of aircraft, each with a different engine. One of the most common types of aircraft engines is the turboprop engine.
A turboprop engine is a type of aircraft engine that uses a gas turbine to drive a propeller. This engine combines two types of engines, a jet engine and a propeller engine. The picture below shows the components of a turboprop engine and how it works.
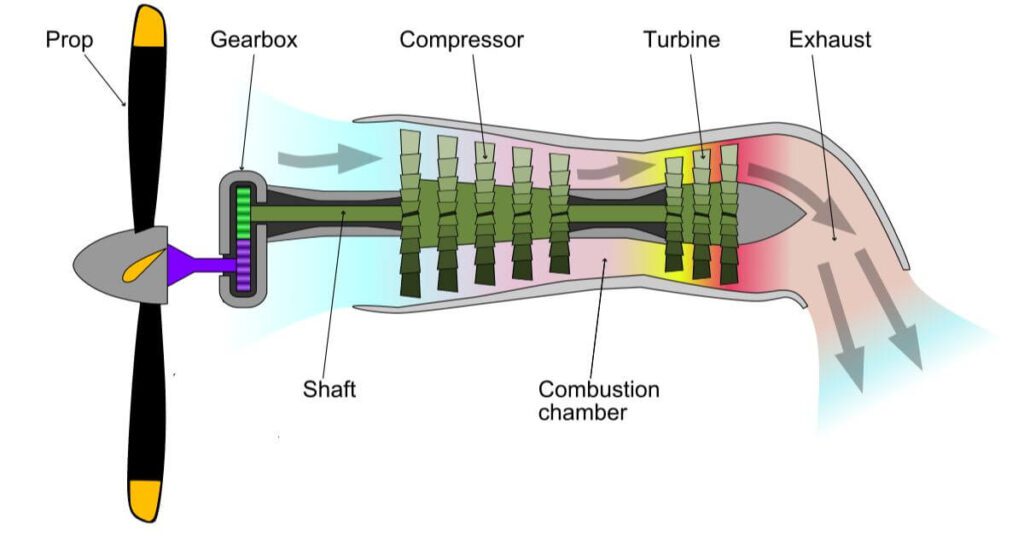
Table of Contents
What are the components of a turboprop engine?
Intake
Intake is a part of an engine that draws air into the engine. Intakes can be either grilles or pipes. Grille intakes are typically used on small turboprop engines, while pipe intakes are typically used on large turboprop engines.
Compressor
A compressor is a part that increases the pressure of air. It consists of multiple stages that increase the pressure of air gradually. Compressors are typically classified as axial or axial-radial compressors. Axial compressors increase the pressure of air directly, while axial-radial compressors increase the pressure of air gradually.
Combustion Chamber
A combustion chamber is a part that is used to burn a mixture of fuel and air. The combustion produces hot gas that has high pressure and temperature. Combustion chambers are typically cylindrical or rectangular in shape.
Turbine
A turbine is a part that converts heat energy into mechanical energy. Turbines typically consist of an exhaust turbine and a compressor turbine. The exhaust turbine is used to drive the propeller, while the compressor turbine is used to drive the compressor.
Propellers
Propellers generate thrust to propel an aircraft. They are coupled to turbines through a reduction gear that converts high torque to high RPM or low torque to low RPM. Propellers are typically made of metal or composite.
Reduction Gears
Reduction gears are parts that function to change high speed. Reduction gears are required to adjust the speed of the propeller to the speed of the aircraft. Reduction gears are typically made of metal or composite.
How does a turboprop engine work?
Compression
Air is drawn into the intake and compressed by the compressor. The compressor consists of multiple stages that function to increase air pressure gradually.
Combustion
Fuel is added to the compressed air in the combustion chamber, where the fuel-air mixture is then burned. Combustion produces hot gases that have high pressure and temperature.
Expansion
Hot gas is expanded through the turbine. The turbine consists of multiple stages that function to convert heat energy into mechanical energy. The mechanical energy generated by the turbine is used to drive the compressor and propeller.
What are the advantages of turboprop engines?
Fuel-efficient
Turboprop engines are more fuel-efficient than other jet engines, such as turbojets and turbofans. It’s because turboprop engines use most of their energy to drive the propeller, which is more efficient than pushing the aircraft using exhaust gases.
Require shorter runways
Turboprop engines can generate significant thrust even at low speeds, so aircraft that use turboprop engines can take off and land on shorter runways.
Suitable for short- and medium-haul flights
Aircraft that use turboprop engines have a lower maximum speed than aircraft that use other jet engines, but they are more suitable for short- and medium-haul flights because they are more fuel-efficient and can operate on shorter runways.
Environmentally friendly
Turboprop engines produce lower exhaust emissions than other jet engines.
Cheaper to maintain
Turboprop engines are cheaper to maintain than other jet engines because it has a simple design.
What are the disadvantages of turboprop engines?
Lower top speed
Aircraft that use turboprop engines have a lower top speed than aircraft that use other jet engines. It’s because the propellers can’t rotate as fast as the fans of other jet engines.
Propeller noise
The propellers of turboprop engines can generate more noise than the fans of other jet engines. This can be disruptive to passengers and residents near airports.
Propeller damage
The propellers of turboprop engines are more vulnerable to damage from foreign objects, such as birds. It’s because the propellers are located outside the engine and rotate at high speeds.
What types of aircraft use turboprop engines?
Commuter aircraft
Commuter aircraft are used to transport passengers over short distances. Turboprop commuter aircraft typically have a passenger capacity of 10 to 50 people. Some examples of turboprop commuter aircraft include the ATR 72, Dash 8, and Saab 340.
Cargo aircraft
Cargo aircraft are used to transport goods. Turboprop cargo aircraft typically have a cargo capacity of 5 to 20 tons. Some examples of turboprop cargo aircraft include the Cessna Caravan, Beechcraft King Air, and Raytheon C-130 Hercules.
Military transport aircraft
Military transport aircraft are used to transport troops and military equipment. Turboprop military transport aircraft typically have a large payload capacity, ranging from 20 to 100 tons. Some examples of turboprop military transport aircraft include the C-130 Hercules, Antonov An-26, and CASA C-212.
Maritime patrol aircraft
Maritime patrol aircraft are used to monitor and secure maritime territory. Turboprop maritime patrol aircraft typically have high speed and range. Some examples of turboprop maritime patrol aircraft include the P-3 Orion, CASA CN-235, and Embraer EMB-120 Brasilia.
In addition to these types of aircraft, turboprop engines are also used in some specialized aircraft, such as ambulance aircraft, firefighting aircraft, and agricultural aircraft.



